How to create and display blocks in Drupal 8
I’m new in the Drupal world, and as many of you maybe run into the situation of how to Create and Display Blocks inside a Form, View, Controller, etc or just using the Admin tool.
I will try to share my experience on how to accomplish this task through this simple post, lets jump into it!
First but not less, we need to understand which kind of Block types we need to create and/or display.
Drupal 8 API provide us 2 groups types of Blocks to create/display.
Content Blocks:
Are Blocks that you create in Drupal Admin Interface.
They are much like Nodes configurable data structures, with Fields etc.
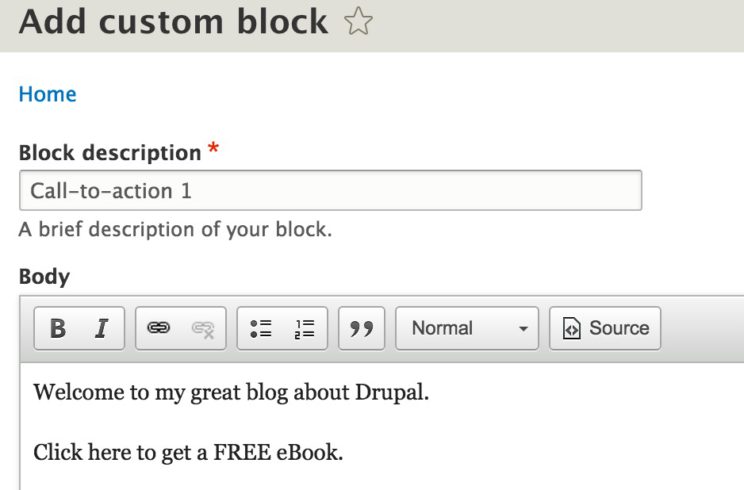
- How to create a Block using the Drupal Interface:
Like Content page, Custom Blocks are now listed on a dedicated page, which uses a Views to list all the entities of type Block.Use the toolbar menu to access that page: Structure -> Block Layout -> Custom Block Library.
In order to create a new Block, click “Add custom Block” and select a Block type.
Blocks are now field-able entities (like Nodes), that’s why you can see different Block types.
and that is it, you created your first Block!
Now, sometime you need to build and display these kind of Block programmatically.
If you want to display one of these, you can do what you would normally do to display Entities, “load” them and “render” them with the View builder.
Let me put words into code:
- How to build Custom Blocks programmatically
$bid = ??? // The block_id $block = \Drupal\block_content\Entity\BlockContent::load($bid); $render = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getViewBuilder('block_content')->view($block); return $render;
Plugin Blocks:
Blocks can also be plugins and created inside Drupal Modules programmatically.
Lets create one:
- How to create plugin Block programmatically:
Once we have created and enabled our custom module , we’ll place our MyBlock.php class under /modules/custom/my_block_example/src/Plugin/Block.
MyBlock.php class will contain:
- Annotation meta data, that will allow us to identify the Block in the Admin section.
If you want to read more about annotations, check read “Annotations-based plugins” on drupal.org - Methods implemented by Plugin interface, in our case only build(). This method will render a renderable array. In our case, we’re returning a basic markup but we could have returned a more complex code, like a form or a views.
<?php namespace Drupal\my_block_example\Plugin\Block; use Drupal\Core\Block\BlockBase; /** * Provides a block with a simple text. * * @Block( * id = "my_block_example_block", * admin_label = @Translation("My block"), * ) */ class MyBlock extends BlockBase { /** * {@inheritdoc} */ public function build() { return [ '#markup' = $this->t('This is a simple block!'), ]; } }
And that is it! We have created a Plugin Block.
Important: One step left is to refresh Drupal cache.
After Block creation you may need to display your Block inside some of the Drupal Entities.
To succeed on this task you will need to call the Block Plugin Manager.
Let’s explain this with code:
- How to build Plugin Blocks programmatically
$block_manager = \Drupal::service('plugin.manager.block'); $config = [];// You can hard code configuration or you load from settings. $plugin_block = $block_manager->createInstance('my_block_example_block', $config); $render = $plugin_block->build(); return $render;
Conclusion:
As you can see, following these simple steps you will be able to create and build any type of Blocks for your Drupal application. I hope you use it and take advantage of all of Drupal API can offer for you.
See you next time!