Entrust for Laravel
Laravel 5.2 comes with user support out of the box but it has a lack of support for roles and permissions. Doing a little of research I found a package to work with Roles and Permissions in Laravel called Entrust (https://github.com/Zizaco/entrust).
This post it’s going to be about the installation, in other post we will cover how to use it and how to create a management UI for users and permissions.
This post asumes that you are currently working in laravel 5.2.
First of all, include the package in composer.json
“require” : {
…
"zizaco/entrust": "5.2.x-dev"
}
Next run composer update to install the new package.
Configuration
Next step is to add the service provider in the app. Add this into the providers array (config/app.php)
Zizaco\Entrust\EntrustServiceProvider::class
Add these entries to the $routeMiddleware array in app/Http/Kernel.php
'role' => Zizaco\Entrust\Middleware\EntrustRole::class,
'permission' => Zizaco\Entrust\Middleware\EntrustPermission::class,
'ability' => Zizaco\Entrust\Middleware\EntrustAbility::class,
In order to work entrust need a configuration file to set the mappings between models and tables. To create the config file run.
php artisan vendor:publish
This will create a file called entrust.php with a default configuration, that configuration will work in most cases.
Entrust uses cache tagging, this kind of caching is not available in file storage, you’ll have to change it to array or memcache. Go to your .env file and check this configuration.
CACHE_DRIVER=memcached
or
CACHE_DRIVER=array
Database Tables
Now generate the Entrust migration:
php artisan entrust:migration
You may now run it with the artisan migrate command:
php artisan migrate
After the migration, four new tables will be present:
- roles — stores role records
- permissions — stores permission records
- role_user — stores many-to-many relations between roles and users
- permission_role — stores many-to-many relations between roles and permissions
Models
You’ll have to create and modify your models to make it work.
Create a Role model inside app/models/Role.php using the following example:
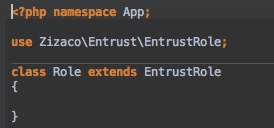
Permission
Create a Permission model inside app/models/Permission.php using the following example: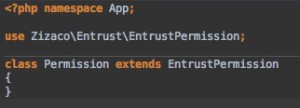
User
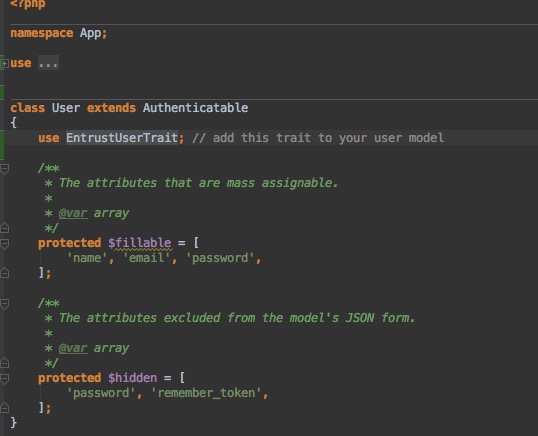
Next, use the EntrustUserTrait trait in your existing User model. For example:
This will enable the relation with Role and add the following methods roles(), hasRole($name), can($permission), and ability($roles, $permissions, $options) within your User model.
Seeding
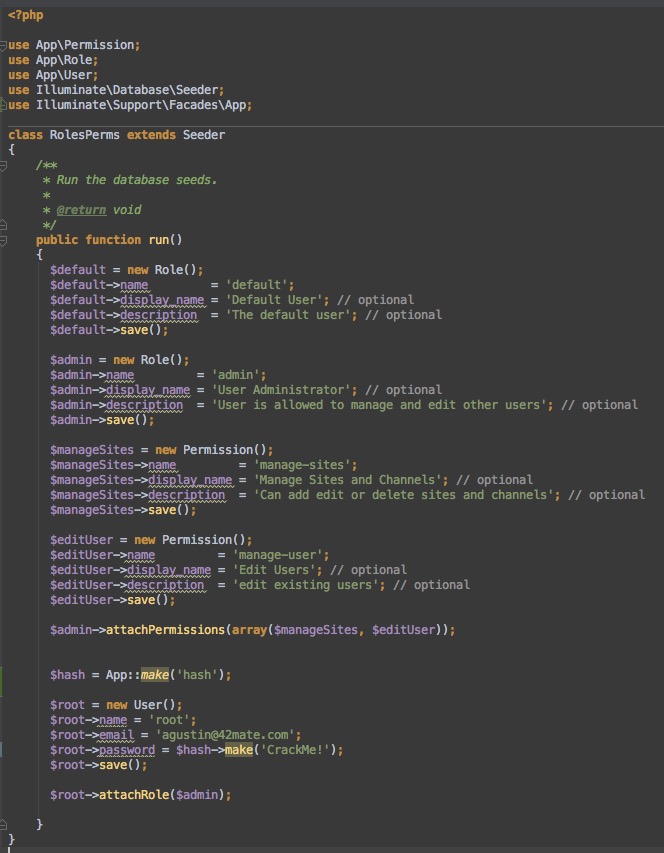
A good idea will be to create a default seed, this it’s going to depend of your project requirements but here is a sample to give you an idea.
Run this artisan command to create a Seeder class
php artisan make:seeder RolesPerms
This will create a seeder file into database/seeds/RolePerms.php
This can be a basic content
To seed this file
artisan db:seed --class=RolesPerms
That’s it, now you are ready to go. We will see in other post how to use this package in our code.


Thanks for the intro, nicely explained.
Looking forward to the next part
hi! where is the other part of the tutorial?